Merkle Tree in blockchain
Apr 29, 2022 By Puneet vermaWhat Is a Merkle Tree?
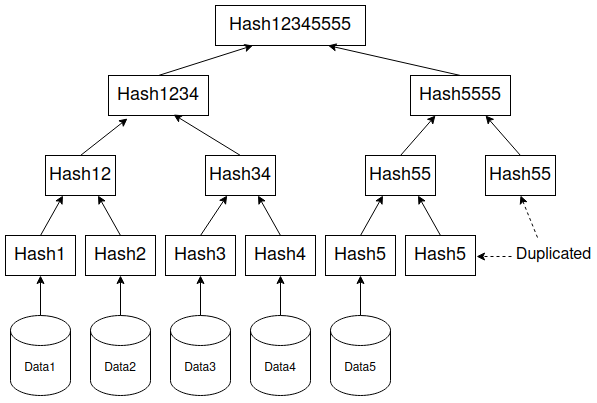
A Merle tree is a data structure that stores the hash of the combined children in each parent. It is also known as a hash tree.
- Merkle Root (or Root Hash): Top node of the tree
- Non-Leaf Nodes: combined hash of data node
- Leaf Nodes: Data node
Merkle root servers as a summary for all data.

How is Merkle root calculated?
It starts with the hash of leaf nodes. Then we combine the hash of the leaf node to get the hash of the parent nodes.
- Let H1 and H2 be the leaf nodes hash
- Parent node will be H12 = hash(H1, H2)
Unbalanced Merkle root
When the last leaf node does have a pair, i.e. when we have an old number of leaf nodes.
This can be handled in many ways. Duplication of the leaf is the most widely used approach.
Duplication: The last leaf node makes pair with itself.
- Let H1, H2 and H3 be the leaf nodes hash
- 1st parent node will be H12 = hash(H1, H2)
- 2nd parent node will be H33 = hash(H3, H3)
Purpose of Merkle tree
It is an efficient and secure way to verify the data.
- Instead of verifying a large set of data bit by bit, we can directly compare their Merkle root
- Even with a single bit change, the hash will be the effect and thereby effects the Merkle root.
Use-Cases of Merkle Tree
- Blockchain
- Git, a version control project-handling software, uses Merkle tree for its repository structure for programmers worldwide.
- Merkle trees are useful in distributed systems where the same data should exist in multiple places
- Merkle trees can be used to check inconsistencies.
- Apache Cassandra uses Merkle trees to detect inconsistencies between replicas of entire databases.
- Interplanetary File System (IPFS) is an open-source, peer-to-peer distributed protocol that uses the Merkle tree for file structure.
- It is used for data replication in No-SQL distributed databases like Amazon DynamoDB.
How Merkle is used in the file-sharing system
Take a scenario where Computer A send data to computer B.
Case 1: When we don't have hash or Merkle tree
computer A sends a file to computer B. How will computer B know whether it got all files?
One way is to send the entire file again and compare both the copies, but what if the file size is huge?.
Case 2: When we have hash
Computer A will send the file plus the hash of that file. On receiving the file, Computer B will also calculate the hash of that file. If both hashes match, computer B received the correct file.
What if hashes are different? We know files are not correct but don't know what is wrong. We need to send the entire file again.
Case 3: When we have Merkle root.
Like case 2: computer A will send the file with the Merkle root, and computer B will calculate the Merkle root.
If it matched, it means the files are correct. If not matched, computer B will request the entire Merkle tree and compare node by node. In this way, computer B will be able to identify which part of the file is wrong and request that portion of file only. This saves our network bandwidth.
Why is Merkle Tree Important For Blockchain?
There is no central authority in the Blockchain network. Each node has the responsibility to ensure the blocks are valid.
- If we don't use the Merkle tree, then all nodes require a full copy of all the transactions. The current size of Bitcoin is 389Gb as of April 2022, which is growing roughly about 10Gb/month.
- To confirm that there were no modifications, a node needs a lot of computing power.
Merkle Trees are a solution to this issue
- Only a small hash is required to transmit over network
- Comparing hashing is very easy as compare to entire data
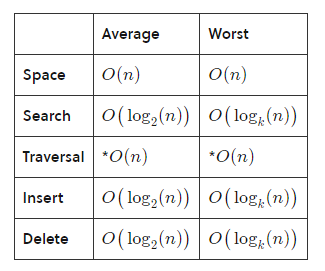
The complexity of Merkl Tree